最近在分析dump时,发现有程序的卡死和WeakReference有关,在以前只知道怎么用,但不清楚底层逻辑走向是什么样的,借着这个dump的契机来简单研究下。
用过WeakReference的朋友都知道这里面又可以分为弱短和弱长两个概念,对应着构造函数中的trackResurrection参数,同时它也是对底层GCHandle.Alloc 方法的封装,参考源码如下:
public WeakReference(object? target, bool trackResurrection){ Create(target, trackResurrection);}private void Create(object target, bool trackResurrection){ nint num = GCHandle.InternalAlloc(target, trackResurrection ? GCHandleType.WeakTrackResurrection : GCHandleType.Weak); _taggedHandle = (trackResurrection ? (num | 1) : num); ComAwareWeakReference.ComInfo comInfo = ComAwareWeakReference.ComInfo.FromObject(target); if (comInfo != null) { ComAwareWeakReference.SetComInfoInConstructor(ref _taggedHandle, comInfo); }}public enum GCHandleType{ // // Summary: // This handle type is used to track an object, but allow it to be collected. When // an object is collected, the contents of the System.Runtime.InteropServices.GCHandle // are zeroed. Weak references are zeroed before the finalizer runs, so even if // the finalizer resurrects the object, the Weak reference is still zeroed. Weak = 0, // // Summary: // This handle type is similar to System.Runtime.InteropServices.GCHandleType.Weak, // but the handle is not zeroed if the object is resurrected during finalization. WeakTrackResurrection = 1}从上面的 GCHandleType 的注释来看。
可能这么说有点抽象,画张图如下:
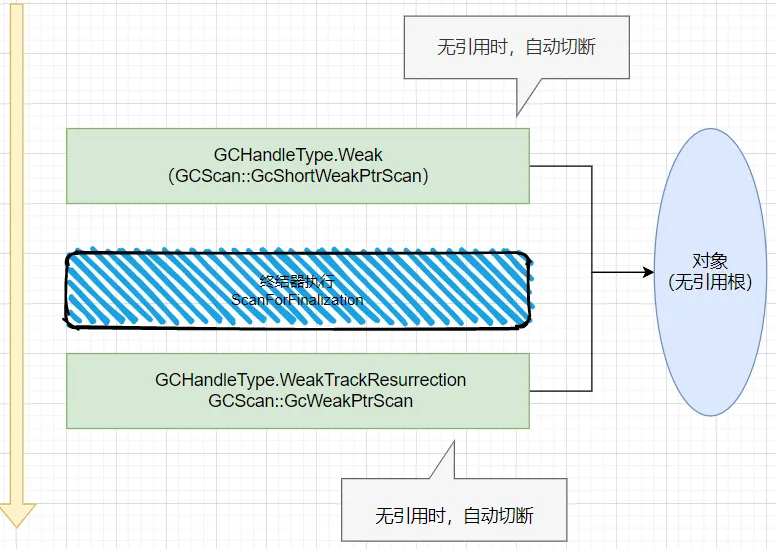 图片
图片
为了方便讲述两者的区别,使用 对象复活 来做测试。
因为在 ScanForFinalization 方法之前做的判断,所以与垃圾对象的联系会被马上切断,参考代码如下:
class Program { static void Main() { WeakReferenceCase(); GC.Collect(); GC.WaitForPendingFinalizers(); Console.WriteLine(weakHandle.Target ?? "Person 引用被切断"); Console.ReadLine(); } public static GCHandle weakHandle; static void WeakReferenceCase() { var person = new Person() { ressurect = false }; weakHandle = GCHandle.Alloc(person, GCHandleType.Weak); } } public class Person { public bool ressurect = false; ~Person() { if (ressurect) { Console.WriteLine("Person 被永生了,不可能被消灭的。。。"); GC.ReRegisterForFinalize(this); } else { Console.WriteLine("Person 析构已执行..."); } } }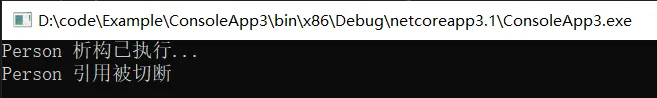 图片
图片
因为是在 ScanForFinalization 之后做的判断,这时候可能会存在 对象复活 的情况,所以垃圾又变成不垃圾了,如果是这种情况就不能切断,参考代码如下:
static void WeakReferenceCase(){ var person = new Person() { ressurect = true }; weakHandle = GCHandle.Alloc(person, GCHandleType.WeakTrackResurrection);}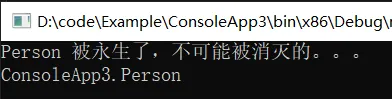 图片
图片
在 coreclr 里有一个 struct 枚举强对应 GCHandleType 结构体,而且名字看的更加清楚,代码如下:
typedef enum{ HNDTYPE_WEAK_SHORT = 0, HNDTYPE_WEAK_LONG = 1,}HandleType;接下来看下刚才截图源码上的验证。
void gc_heap::mark_phase(int condemned_gen_number, BOOL mark_only_p){ // null out the target of short weakref that were not promoted. GCScan::GcShortWeakPtrScan(condemned_gen_number, max_generation, &sc); dprintf(3, ("Finalize marking")); finalize_queue->ScanForFinalization(GCHeap::Promote, condemned_gen_number, mark_only_p, __this); // null out the target of long weakref that were not promoted. GCScan::GcWeakPtrScan(condemned_gen_number, max_generation, &sc);}BOOL CFinalize::ScanForFinalization(promote_func* pfn, int gen, BOOL mark_only_p, gc_heap* hp){ for (unsigned int Seg = startSeg; Seg <= gen_segment(0); Seg++) { Object** endIndex = SegQueue(Seg); for (Object** i = SegQueueLimit(Seg) - 1; i >= endIndex; i--) { CObjectHeader* obj = (CObjectHeader*)*i; if (!g_theGCHeap->IsPromoted(obj)) { if (method_table(obj)->HasCriticalFinalizer()) { MoveItem(i, Seg, CriticalFinalizerListSeg); } else { MoveItem(i, Seg, FinalizerListSeg); } } } } if(finalizedFound) GCToEEInterface::EnableFinalization(true); return finalizedFound;}源码中有几个注意点:
gc 在标记时,将有根的对象mt的第一位设为 1 来表示当前已经标记过,即有用对象,未被标记的即为垃圾对象。
从简化的源码看,一旦有垃圾对象被送入到 终结器队列的 预备区 时,就会通过 GCToEEInterface::EnableFinalization(true) 启动终结器线程,所以在测试代码中加了 GC.WaitForPendingFinalizers(); 就是为了等待终结器线程执行完毕然后才判断 Target,这样结果就会更加准确。
有些朋友会好奇那个 weakHandle.Target=null 的逻辑到底在 coreclr 的何处,这个比较简单,可以用 windbg 下 ba 断点即可,我们还是拿弱引用来举例,截图如下:
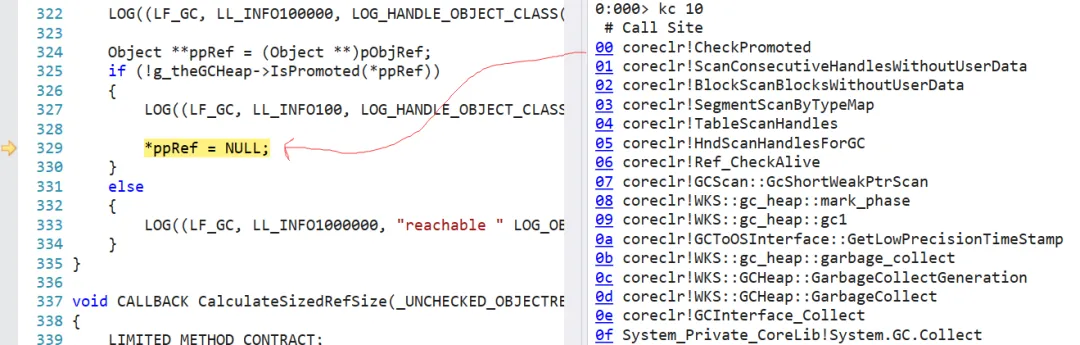 图片
图片
WeakReference 的内部玩法有很多,更深入的理解还需要对 g_HandleTableMap 进行深度挖掘,后面有机会再聊吧,有时候dump分析还是挺苦逼的,需要对相关领域底层知识有一个足够了解,否则谈何修复呢?
本文链接:http://www.28at.com/showinfo-26-97278-0.html聊一聊 C# 弱引用底层是怎么玩的
声明:本网页内容旨在传播知识,若有侵权等问题请及时与本网联系,我们将在第一时间删除处理。邮件:2376512515@qq.com